Introduction
Am writing this to demonstrate how to leverage the
powerful features of Oracle database and build a simple application from it.
The application programming language used in this is the .Net, First things
first, why oracle?
Oracle offers the industry most complete and
integrated set of tools for application development, database development, and
business intelligence to support any development approach, technology platform,
or operating system. Next question…why bother write this?
As an
application programmer we yarn to have a smooth running application with no
downtime, able to swiftly handle error exceptions, transactions capability,
make use of oracles pl/sql (I think it’s the only one having the procedural
language extension) etc.
Prerequisites
Ø Microsoft
Visual Studio (Using 2008)
Ø Oracle
11g
Ø Oracle
Data Access Components with Oracle Developer Tools
Ø Oracle
developer tool for visual studio.
What
I intend to show you
Ø Connecting
to Oracle 11g.
Ø Integrate
an application to Oracle
Ø Creating
a dynamic link library to handle crude operations to your oracle database.
Oracle
SQL Developer
This is a free integrated development environment
that simplifies the development and management of Oracle Database in both the
traditional and cloud deployments. It will help in the complete end to end
development of the pl/sql applications that you create not mentioning more
features like a nice worksheet to run your queries.
Create your connections on this screen. Oops must
have forgotten to show you how to install oracle 11g and the Oracle developer
but I think that can be too basic for however finds this useful.
Once successfully creating your connection, and
database, create a table as shown below:
Hoping you have your visual basic Integrated
development environment ready, Just click on start menu and open in (this is
here the ball meats the road.)
.NET Data Provider
Data provider is the layer between the .Net
application code and the Oracle client connectivity software. .NET applications
require the use of a managed data provider (managed by the .NET framework).At
this point install the Oracle Developer Tools for Visual Studio:
Installation is straight forward jus follow the
wizard:
On the visual studio we will now create a new
Project,
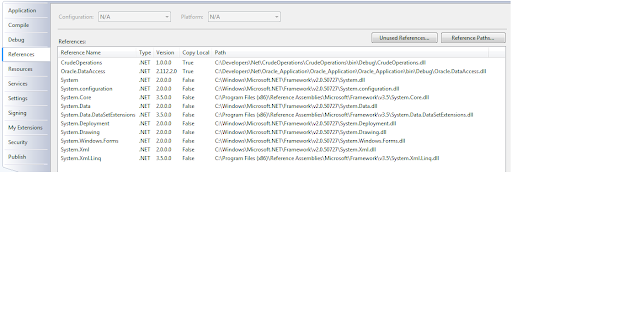
This is a crude application that we will integrate
to the oracle database.Your application references should look something like
this.
At the top is a reference CrudeOperations,this is a .dll that we will build later that will simplify
our calls for database access,for now open the config file (app.config).If it
does not exist quickly add it,I prefer my connections in the app.config file
for easy of deployment where you can easily edit your connection string.The
app.config file should look like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<!-- required to
use a oracle.dataaccess.client configuration setting -->
<configSections>
<section
name="oracle.dataaccess.client"
type="System.Data.Common.DbProviderConfigurationHandler, System.Data,
Version=2.0.0.0, Culture=neutral,
PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" />
</configSections>
<!-- here are
some example settings to be passed to the provider. refer
to the docs for a complete list -->
<oracle.dataaccess.client>
<settings>
<add name="FetchSize"
value="65536"/>
<add name="TraceFileName"
value="c:\myodpnet.trc"/>
<add name="TraceLevel"
value="0"/>
<add name="TraceOption"
value="0"/>
<!--<add name="DllPath"
value="C:\testcases\unzipdeploy\folder1"/>-->
</settings>
</oracle.dataaccess.client>
<appSettings>
<add key="constring"
value="user id=system;password=1234;data
source=localhost" />
</appSettings>
<system.diagnostics>
<sources>
<!--
This section defines the logging configuration for My.Application.Log -->
<source
name="DefaultSource" switchName="DefaultSwitch">
<listeners>
<add
name="FileLog"/>
<!--
Uncomment the below section to write to the Application Event Log -->
<!--<add
name="EventLog"/>-->
</listeners>
</source>
</sources>
<switches>
<add
name="DefaultSwitch" value="Information" />
</switches>
<sharedListeners>
<add name="FileLog"
type="Microsoft.VisualBasic.Logging.FileLogTraceListener,
Microsoft.VisualBasic, Version=8.0.0.0, Culture=neutral,
PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a, processorArchitecture=MSIL"
initializeData="FileLogWriter"/>
<!--
Uncomment the below section and replace APPLICATION_NAME with the name of your
application to write to the Application Event Log -->
<!--<add
name="EventLog" type="System.Diagnostics.EventLogTraceListener"
initializeData="APPLICATION_NAME"/> -->
</sharedListeners>
</system.diagnostics>
</configuration>
Just explaining the crucial part is this line:
<add key="constring" value="user id=system;password=1234;data source=localhost" />
This gives the connection string to your oracle
database,for
non demo applications,more features are needed in this config file to
make it more secure.
Let’s
build the .dll
On your visual basic development,create
a new project,this time it should be a class library as shown below.
The class library will be the class containing
operation to the database,the reference should look
something like this:
Note the first reference as Oracle.DataAccess, which
provides connectivity to the oracle instance.
Add these lines to your class:
Imports System.Configuration
Imports
Oracle.DataAccess.Types
Imports
Oracle.DataAccess.Client
Imports System.Data.SqlClient
This imports all references that we need in our
functions (can’t explain them all since it’s beyond my scope for now)
The function that does connection to my Oracle database :
Public Function doConnect()
Dim con As OracleConnection = New OracleConnection()
Dim constr As String = System.Configuration.ConfigurationManager.AppSettings("constring")
con = New
OracleConnection(constr)
con.Open()
Return con
End Function
Remember to also include the app.config here,since its necessary to avoid compilation erros when
building your .dll.
The next function will perfom an adition of an item
in the oracle database table:
Public Function doAdd(ByVal columnString, ByVal valueString, ByVal addtable,
ByVal increamentColumn)
Dim cn As New
Operations
Dim myConn = cn.doConnect()
'Dim tr As OracleTransaction
Dim insertedInt As
Integer = 0
'cmdDEl.CommandText =
"DROP SEQUENCE person_sequence"
Dim cmdSeq As
OracleCommand = New OracleCommand("",
myConn)
cmdSeq.CommandText =
"DECLARE v_holder
NUMBER; BEGIN SELECT 1 INTO v_holder
FROM user_sequences
WHERE sequence_name =
'" & addtable & "_SEQUENCE'; EXCEPTION WHEN no_data_found
THEN EXECUTE IMMEDIATE
'create sequence " & addtable & "_SEQUENCE';END;"
cmdSeq.ExecuteNonQuery()
Dim cmdTrigger As
OracleCommand = New OracleCommand("",
myConn)
cmdTrigger.CommandText
= "CREATE OR REPLACE trigger tt_" & addtable &
"
BEFORE INSERT ON "
& addtable & " for each row BEGIN SELECT
" & addtable & "_SEQUENCE.nextval
INTO
:new." & increamentColumn
& " FROM dual; end;"
cmdTrigger.ExecuteNonQuery()
'
create the command object
Dim cmd As
OracleCommand = myConn.CreateCommand()
cmd.CommandText =
"INSERT INTO " & addtable & "
(" & columnString & ") values (:1)"
'
create a parameter for the name
Dim p_name As
OracleParameter = New OracleParameter
p_name.Value =
valueString
'
add the parameter to the collection
cmd.Parameters.Add(p_name)
'
execute the insert
'
the trigger will supply the value for the "id" column
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery()
Dim cmdNext As
OracleCommand = New OracleCommand("",
myConn)
cmdNext.CommandText =
"SELECT " & addtable & "_SEQUENCE.CURRVAL FROM dual"
Dim dr As
OracleDataReader = cmdNext.ExecuteReader()
dr.Read()
insertedInt
= dr.Item("CURRVAL")
cmdNext.Dispose()
cmdSeq.Dispose()
cmdTrigger.Dispose()
'' clean
up
p_name.Dispose()
cmd.Dispose()
myConn.Dispose()
Return insertedInt
End Function
The parameters sent to this function are:
Ø columnString
= this gives a single column that you would like some default data inserted.
Ø valueString
= value for that default column.
Ø Addtable
= the table to perform the addition
Ø increamentColumn
= the increment column.
In Oracle I use this form of incrementing , using
sequence and triggers to be safe in backward compatibility , latest Oracle
database already have an identity column , that help you easily do an auto
increment in a column.
Rest of the functions are
pretty straight forward:
Public Function getFormSingleTable(ByVal myIndex, ByVal myIndexValue, ByVal
mySelectTable)
Dim cn As New
Operations
Try
Dim myConn = cn.doConnect()
Dim cmd As
OracleCommand = New OracleCommand("",
myConn)
cmd.CommandText =
"SELECT * FROM " & mySelectTable & "
WHERE " & myIndex & " = '" & myIndexValue
& "'"
Dim dReader As OracleDataReader = cmd.ExecuteReader()
dReader.Read()
Return dReader
myConn.Dispose()
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox("Failed
to connect to data source : " & ex.Message)
Return 0
End Try
End Function
This fetches from a table returning the data reader
object which you can insert in your forms like
Textbox1.text = dReader.Item(“FirstName”);
Pretty simple, I guess
Next is a function to perform Delete:
Public Function doDelete(ByVal myColId, ByVal myValue, ByVal mytable)
Dim cn As New
Operations
Try
Dim myConn = cn.doConnect()
Dim cmd As
OracleCommand = New OracleCommand("",
myConn)
cmd.CommandText =
"DELETE FROM " & mytable & "
WHERE " & myColId & " = " & myValue &
""
cmd.ExecuteReader()
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox("Failed
to connect to data source : " & ex.Message)
Return 0
End Try
Return myColId
End Function
Function remaining is the Update function,as shown below:
Public Function doUpdate(ByVal
myQuery)
Dim cn As New Operations
Try
Dim myConn = cn.doConnect()
Dim cmd As OracleCommand = New OracleCommand("", myConn)
cmd.CommandText = myQuery
cmd.ExecuteReader()
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox("Failed
to connect to data source : " & ex.Message)
Return 0
End Try
Return myQuery
End Function
To populate a grid I have created a function below
that does my job swiftly:NB I will post a full class
where this .dll is made use no need of panic this early. The populate grid is
as shown below:
Public Function doPopulateGrid(ByVal
myQuery, ByVal gridObject)
Dim cn As New Operations
Dim rowCount As String = ""
Try
Dim Connection = cn.doConnect()
Dim command As OracleCommand
Dim adapter As OracleDataAdapter
Dim builder As OracleCommandBuilder
Dim userTable As DataTable
Dim ds As
DataSet
Dim gridDataTable As New
Data.DataTable
command =
New OracleCommand(myQuery, Connection)
adapter =
New OracleDataAdapter(command)
builder =
New OracleCommandBuilder(adapter)
ds = New
DataSet()
adapter.Fill(ds)
userTable
= ds.Tables(0)
gridObject.DataSource =
userTable.DefaultView
rowCount =
userTable.Rows.Count.ToString()
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox("Failed
to connect to data source : " & ex.Message)
Return 0
End Try
Return rowCount
End Function
After adding all this functions, build your class
library, I hope no error, If there is no error we are
good to use the .dll in the Oracle_Application we first created. Navigate to
that VB.Net Project, and add the Operations.dll as Project Reference.
Click on browse and navigate where we have built the
class library.
(After building the class library you should have
the .dll ready in your build folders)
I will now post how the Form.vb class in the
Oracle_Application should now look like below:
Imports
System
Imports
System.Data
Imports
Oracle.DataAccess.Client
Imports
System.Configuration
Imports
Oracle.DataAccess.Types
Imports Operations
Imports
Oracle_Application.Connection
Public
Class Form1
Dim Connection As
OracleConnection
Dim command As OracleCommand
Dim adapter, adapter1, adapter2 As
OracleDataAdapter
Dim builder As OracleCommandBuilder
Dim ds As DataSet
Dim userTable As DataTable
Public Sub dofill()
Dim appObject As New Operations
Connection = appObject.doConnect
Try
Dim sqlQuery = "SELECT P.ID,P.FIRSTNAME,C.COMPANYNAME FROM PERSON P, COMPANY C
WHERE C.PERSON_ID= P.ID ORDER BY
P.ID ASC"
Dim gridDataTable As New
Data.DataTable
command =
New OracleCommand(sqlQuery, Connection)
adapter =
New OracleDataAdapter(command)
builder =
New OracleCommandBuilder(adapter)
ds = New
DataSet()
adapter.Fill(ds)
userTable
= ds.Tables(0)
DataGridView1.DataSource =
userTable.DefaultView
With DataGridView1
.RowHeadersVisible = False
.Columns(0).HeaderCell.Value
= "id"
.Columns(0).Width
= 100
.Columns(0).AutoSizeMode
= DataGridViewAutoSizeColumnMode.NotSet
.Columns(1).HeaderCell.Value
= "names"
.Columns(1).AutoSizeMode
= DataGridViewAutoSizeColumnMode.Fill
.Columns(2).HeaderCell.Value
= "company"
.Columns(2).AutoSizeMode
= DataGridViewAutoSizeColumnMode.Fill
End With
DataGridView1.MultiSelect = True
DataGridView1.SelectionMode =
DataGridViewSelectionMode.FullRowSelect
DataGridView1.Rows(DataGridView1.Rows.Count
- 2).Selected = True
DataGridView1.Select()
DataGridView1.AutoResizeColumns()
DataGridView1.AutoSizeColumnsMode =
DataGridViewAutoSizeColumnsMode.AllCells
lblRowCount.Text = "Number of
records: " + userTable.Rows.Count.ToString()
Catch ex As Exception
'MsgBox("Error
:" & ex.Message)
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub Form1_Load(ByVal
sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Me.Load
doFill()
End Sub
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal
sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim appObject As New Operations
Try
'Dim dr = appObject.getFormSingleTable("id",
TextBox1.Text, "PERSON")
Dim myQueryString As String =
"SELECT P.FIRSTNAME,C.COMPANYNAME FROM
PERSON P, COMPANY C WHERE C.PERSON_ID= P.ID AND P.ID = '" &
TextBox1.Text & "'"
Dim dr = appObject.getFormMultipleTable(myQueryString)
TextBox2.Text = dr.Item("FIRSTNAME")
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox("Error
: " & ex.Message)
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub Button3_Click(ByVal
sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button3.Click
Try
Dim appObject As New Operations
Dim insertId As Integer
insertId =
appObject.doAdd("FIRSTNAME", TextBox2.Text, "PERSON",
"ID")
Console.WriteLine("Inserted
id is : " & insertId)
appObject.doAdd("PERSON_ID",
insertId, "COMPANY", "ID")
DataGridView1.MultiSelect = False
dofill()
TextBox1.Text = insertId
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox(ex.Message)
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnUpdate_Click(ByVal
sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnUpdate.Click
Dim appObject As New Operations
Dim rowIndex =
DataGridView1.CurrentRow.Index
Dim rowId = DataGridView1.Rows(rowIndex).Cells(0).Value
If Connection.State =
ConnectionState.Open Then
Connection.Close()
Else
Connection.Open()
End If
Try
Connection.Open()
Dim cmd = New OracleCommand("UPDATE
PERSON set FIRSTNAME = :1 WHERE ID = " & rowId & "",
Connection)
Dim p1 = cmd.Parameters.Add("COL1_Parameter",
"")
p1.Value = ds.Tables(0).Rows(rowIndex)(1)
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery()
MsgBox("Saved!")
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox("Error
:" & ex.Message)
Finally
Connection.Close()
End Try
'adapter.Update(userTable)
End Sub
Private Sub btnDelete_Click(ByVal
sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnDelete.Click
Dim confirm As Integer
Dim appObject As New Operations
confirm =
MessageBox.Show("Do you really want to delete the selected
record(s)?", "Delete records", MessageBoxButtons.YesNo,
MessageBoxIcon.Warning, MessageBoxDefaultButton.Button2, 0, False)
If (confirm = DialogResult.Yes) Then
If Connection.State =
ConnectionState.Open Then
Connection.Close()
Else
Connection.Open()
End If
Dim cntSelected As Integer = 0
cntSelected
= DataGridView1.SelectedRows.Count
Try
For i As Integer = 1 To cntSelected
If
(DataGridView1.SelectedRows.Count > 0 And DataGridView1.SelectedRows(0).Index
<> DataGridView1.Rows.Count - 1) Then
Try
Dim rowId = DataGridView1.Rows(DataGridView1.SelectedRows(0).Index).Cells(0).Value
appObject.doDelete("PERSON_ID",
rowId, "COMPANY")
appObject.doDelete("ID",
rowId, "PERSON")
'adapter.Update(userTable)
DataGridView1.MultiSelect = True
DataGridView1.SelectionMode = DataGridViewSelectionMode.FullRowSelect
DataGridView1.Rows(DataGridView1.Rows.Count
- 2).Selected = True
DataGridView1.Select()
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox("Error
:" & ex.Message)
End Try
DataGridView1.Rows.RemoveAt(DataGridView1.SelectedRows(0).Index)
End If
Next
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox("Error
:" & ex.Message)
Finally
Connection.Close()
End Try
Else
End If
End Sub
End
Class
You should now have it working as below:
Thanks! And your opinions on it all welcomed!









No comments:
Post a Comment